




Welding is one of the largest application fields for industrial robots.
In the world of industrial robots, the usage of welding robots can account for about 50%. Whether it is automobile production, electronic manufacturing, or engineering machinery and urban construction, the assistance of welding robots is indispensable.
I. Modern Welding Emerged Alongside the Industrial Revolution
Welding is an ancient and traditional craft that dates back 5,000 years.
Around 3000 BCE, Egypt saw the emergence of forge welding techniques; by 1600 BCE, the Shang Dynasty in China used cast welding to manufacture weapons; and by 200 BCE, China had mastered the brazing of bronze and the forge welding of iron artifacts.
Modern welding began with the discovery of the electric arc by the British, coinciding with the Industrial Revolution.
In 1801, the British H.Davy discovered the electric arc; in 1856, the English physicist James Joule discovered the principle of resistance welding; in 1881, the Frenchman De Meritens invented the earliest carbon arc welding machine; four years later, the Pole Benardos Olszewski developed carbon arc welding technology; in 1888, the Russian H.г.Cлавянов invented metal-arc welding.
It was not until then that the American C.L.Coffin first practically used a welding wire as an electrode for electric arc welding.
Since then, welding-related processes have taken off, with the invention of various techniques such as AC welding, surfacing welding, atomic hydrogen welding, and submerged arc welding. In 1931, a symbol of mature welding technology—the Empire State Building, composed of a steel structure made by welding—was completed. To this day, the Empire State Building remains one of the timeless landmarks of New York.
However, modern welding in China did not begin until 1952, after the founding of the People's Republic of China.
In 1952, the first welding teaching and research section in China—the Harbin Institute of Technology Welding Teaching and Research Section—was officially established; four years later, the Harbin Welding Institute was founded; in 1962, the Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society established the Welding Association, which published welding textbooks and held the first National Welding Conference in Harbin that year.
In 1964, China became a full member of the International Institute of Welding, integrating the Chinese welding industry with the world.
Since then, the development of modern welding in China has accelerated. In 1970, the thyristor inverter welding machine was introduced; in 1987, the China Welding Association was established in Beijing; in 1989, the Harbin National Key Laboratory for Modern Welding Production Technology was established; from 1983 to 1991, the Chengdu Electric Welding Machine Research Institute, Tsinghua University, Harbin Institute of Technology, and South China University of Technology successively introduced various types of inverter welding machines with switching devices.
In 1990, high-frequency inverter technology made significant progress with the development of 100KHz MOSFET inverter welding machines, which were applied to the civil welding machine market; in 2000, IGBT single-tube inverter welding machines were widely applied to the civil welding machine field; in 2007, Chinese welding scholars and manufacturers began to research and apply digital (including semi-digital) welding machines.
During this period, a number of welding experts and leaders emerged in China, such as Academician Pan Jiluan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Academician Guan Qiao of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, Academician Xu Binshi of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and Academician Lin Shangyang of the Chinese Academy of Engineering.
II. Diverse Applications of Welding
In fact, as early as the last century, welding had been applied in various fields such as industry, automotive, construction, military, shipbuilding, and aerospace.
In the automotive field, in 1933, the first all-welded structure FORD brand car made with arc welding and resistance welding technology came off the production line; in the construction field, the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, the world's highest suspension bridge, was completed and opened to traffic, with 87,750 tons of steel welded for the bridge; in the military field, during World War II, the manufacturing of warships, aircraft, tanks, and various heavy weapons all used a large amount of welding technology; in the shipbuilding field, in 1956, China's first self-designed and built ten-thousand-ton ocean-going ship "Dongfeng" was successfully delivered; in the aerospace field, in 1970, the Long March 1 successfully launched China's first artificial Earth satellite "Dong Fang Hong 1."
Entering the 21st century, with the increasing complexity of industrial scenarios and the vigorous development of the new energy industry, welding technology has been widely applied in fields such as metallurgy, petroleum, electronic equipment, new energy vehicles, new energy batteries, and container manufacturing. At the same time, welding robots have also ushered in a true technological innovation. With the aid of optical sensor technology and intelligent control systems, the new generation of welding robots has shown stronger adaptability and higher precision, capable of seamless docking with the production line, real-time monitoring, and optimizing the welding process to ensure product quality. Notably, by ingeniously integrating advanced technologies such as machine vision and laser tracking, the intelligence, autonomy, and flexibility of welding robots have been significantly enhanced, becoming an important driving force for the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry.
According to insiders, the development of shipbuilding, new energy vehicles, and steel structure welding is currently most promising.
Steel structures are widely used in downstream industrial plants, high-rise and super high-rise buildings, terminals, railway stations, thermal power plants, bridges, and other fields. In July 2020, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, in conjunction with multiple departments, issued the "Green Building Initiative Action Plan," which proposed "to vigorously develop prefabricated buildings such as steel structures, and new public buildings should use steel structures in principle." The demand for welding will gradually increase with the demand for steel structures.
The welding industry places great emphasis on the adaptability to scenarios. Faced with complex working environments, different welding materials, and various levels of welding requirements, a variety of welding processes have been developed, which can be roughly divided into three major categories—fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing.
Among them, arc welding can be widely used for the welding of various metal products and is currently the most extensive welding method in industrial production. The steel structure field generally adopts arc welding methods. Some industry insiders believe that arc welding is easy to start with, but it is very difficult to do well.
Laser welding has high precision and is suitable for the welding of miniature parts. Due to the simple operation of handheld laser welding products, their application has become more and more widespread in recent years.
Pressure welding is divided into resistance welding, friction welding, diffusion welding, and high-frequency welding.
In resistance welding, spot welding, which is mainly used for thin plate welding, is reflected in parts such as the car cab and carriage, making spot welding technology the most common in the automotive field.
Brazing is divided into three processes: soldering iron brazing, flame brazing, and furnace brazing. Its characteristics include low energy consumption, short time, low temperature, and low cost, but it can only weld the same or similar metal materials, and the welding strength is relatively low.
From the diversity of welding scenarios and welding technologies, it can be seen that the manufacturing of welding robots is not easy.
III. Mobile Welding Robots Revolutionize the Field of Intelligent Welding
With the development of China's welding technology and the advancement of industrial automation, fixed welding robots can no longer meet complex welding needs. Robots are no longer simply executing commands but have begun to learn to predict and judge and adapt to complex environments. With the support of artificial intelligence algorithms, in addition, integrated design, multifunctionality, and ease of operation and maintenance, these robots can even achieve self-learning and gradually optimize their own action strategies.
Mobile welding robots, as an important part of the industrial automation field, have developed and applied rapidly in recent years. These robots combine advanced mechanics, electronics, computer, and sensor technologies to achieve automated and intelligent welding operations. Compared with traditional fixed welding robots, mobile welding robots can move and operate freely within the working area, thus being able to automatically complete the assigned welding tasks without manual auxiliary operations. They are an efficient, flexible, and intelligent automated welding tool that can greatly improve production efficiency and quality, and reduce manual intervention and costs. With the rise of the mobile welding robot market, many enterprises in the welding industry chain have emerged and successfully gone global.

According to research, the trend towards intelligent and automated welding robots is becoming increasingly strong, with their products evolving from taught robots to those that require no teaching.
LE Robotics focuses on mobile welding robots, equipped with SLAM autonomous navigation, 3D vision, and robotic control technology, which have been widely used in the steel structure industry to create steel construction welding solutions.

(1) SLAM Autonomous Navigation
LE Robotics' SLAM autonomous navigation features include high-precision positioning, real-time map building and updating, intelligent obstacle avoidance, path optimization, adaptability to complex environments, simple user interaction, and real-time data synchronization and feedback. These ensure that welding operations are safe, efficient, and accurate in various working scenarios.
(2) 3D Vision for Programming and Teaching-Free Operation
With advanced 3D vision technology and image processing algorithms, LE Robotics can automatically recognize and plan welding paths without manual operation guidance. It is particularly suitable for welding of small batches and non-standard workpieces, offering breakthrough advantages in work efficiency and welding precision. Especially popular in industries such as steel structure, towers, ships, and heavy industry, it can meet the huge demand for teaching-free robots in these industries, further optimizing production processes and reducing labor costs.
(3) AI Technology
By integrating advanced AI voice and gesture recognition technologies, users can directly control the robot with voice commands and gestures, completely replacing the traditional keyboard input method. This innovative human-robot interaction not only improves the convenience and efficiency of operation but also greatly reduces the learning curve, allowing operators to focus more on the welding itself. Particularly suitable for work environments that require frequent adjustments and high flexibility, it provides intelligent solutions for complex industrial applications such as steel structure, shipbuilding, and heavy industry, enhancing the overall safety and convenience of operations.
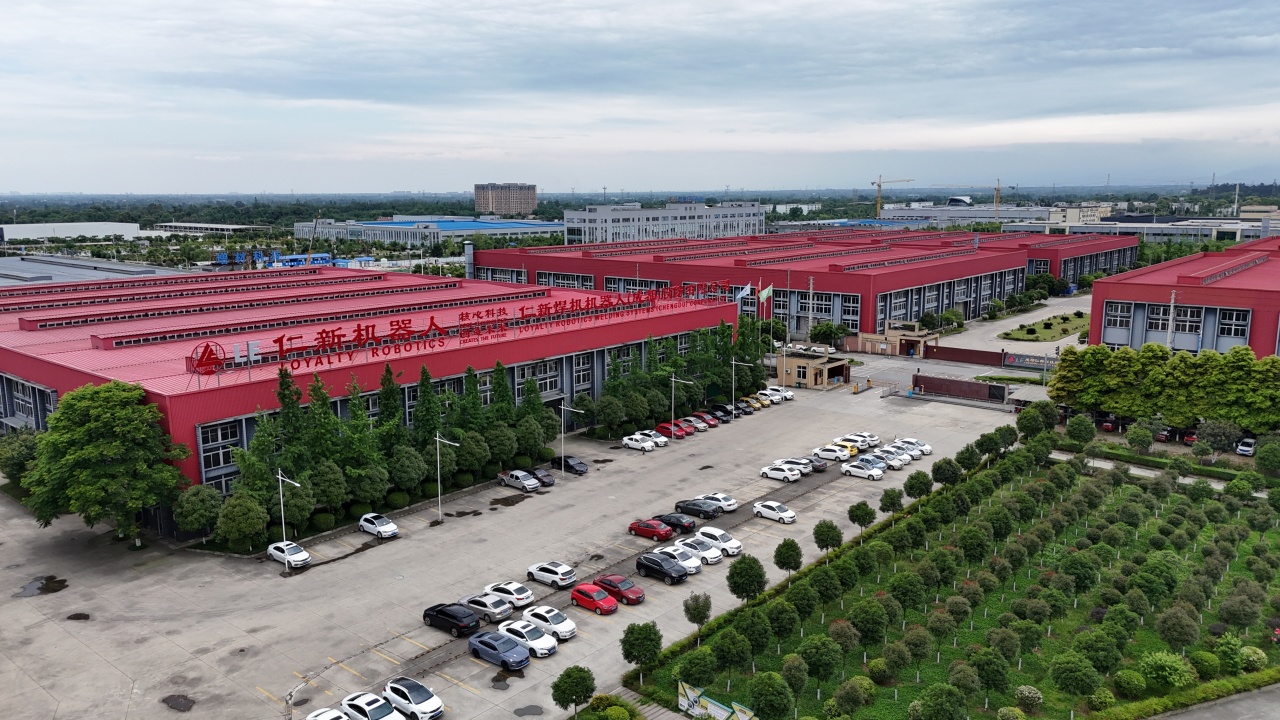

With the continuous advancement of technology, LE Robotics is expected to occupy a more important position in the welding industry. By persistently promoting technological innovation, it will meet the needs of the future market and play a greater role in the field of intelligent manufacturing.
We sincerely invite you to contact us to learn more about LE Robotics, or arrange for a product demonstration. Cooperate with LE Robotics to seize the opportunities in intelligent manufacturing and create a better future together.
——END——
Contact